Data visualization is a way to represent information graphically that highlights patterns and trends and enables viewers to get quick insights. Color, brightness, size, shape, and motion of visual objects are used to present data, which aid interpretation in ways that just text or numbers or simple graphs do not. The visualization options go far beyond the traditional pie-charts, bar and line graphs, and include scatter plots, Mekko charts, heat maps, bubble clouds, Venn diagrams and more.
Data visualization is growing in importance as we collect more and more data, to the point where we are practically drowning and it’s hard to tell what is important and what isn’t. Let’s consider the product development program for a new car or aircraft. Analyzing test data is critical, but with every test drive or flight, such a huge volume of data is generated, making it difficult to process at the speed needed. Visualization techniques help us to understand such complex data and notice patterns or anomalies.
We can see the power of visualization in the example from history which first applied visualization to help citizens understand a government budget. Most government budgets are complex, obscure and difficult to fathom, but the interactive treemap below, created by the Obama administration in 2016, allowed users to see the allocations to different program areas and also get more information about them.
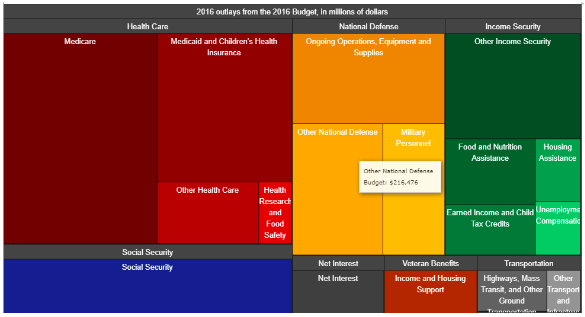
Over time, the availability of more powerful computing power and software have helped to create more and more sophisticated visualization techniques for larger and larger datasets.
Here is one more example. Taken from Tableau Public, this dashboard template created by Chantilly Jaggernauth, could be used by sports organizations such as the #NBA to easily track their ticket sales throughout the season.
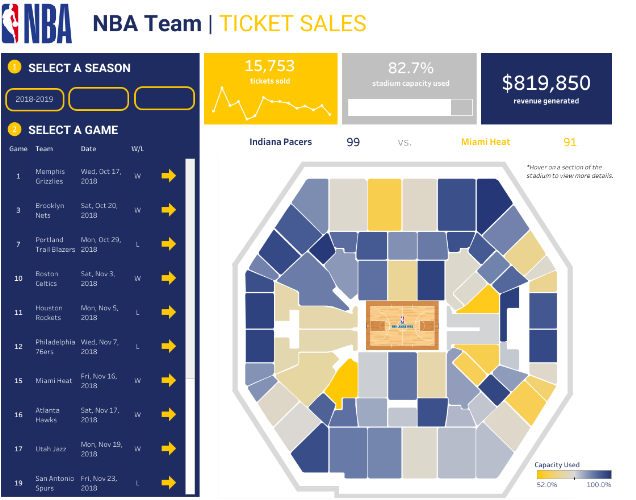
Note: All data used is fake and does not reflect actual revenue, capacity, or ticket sales for the NBA or any NBA organization.
Not just pretty pictures: data visualization works for your business
Why should you apply data visualization techniques to the diverse kinds and vast amounts of data generated throughout your business? Simply put: because every kind of organization benefits from making data easier to understand; businesses across sectors, and also government, education, healthcare, and sports organizations.
Some of the methods used in data visualization today include area chart, bar chart, box-and-whisker plots, bubble cloud, bullet graph, cartogram, circle view, dot distribution map, Gantt chart, heat map, highlight table, histogram, matrix, network, polar area, radial tree, scatter plot (2d or 3d), streamgraph, text tables, timeline, treemap, wedge stack graph, and word cloud. You can choose the right type of visualization based on the purpose of your visualization, the nature of data, and the needs of your audience.
Let’s look at the benefits of data visualization for business.
- Instant absorption of large and complex data
When presented effectively, we are able to grasp large volumes of data literally in the blink of an eye. The reason for this is that the neural process required to process ready images is much easier than creating our own visualization from text or numbers. We are also able to appreciate the interrelations between different data points more easily when we view their visual representations. Once we see something, we internalize it faster.
Our addiction to our smartphone or tablet screens has led to shortened attention spans, so receiving information as a ‘snapshot’ is helpful. On the other hand, if you have systems in your organization to collect data but no effective way to present it to stakeholders, then you are unlikely to get the expected business benefits, as users struggle to make sense of unwieldy and hard-to-understand reports.
So a data visualization creates small ‘packages’ or units of information to convey sets of ideas that can be stored in your viewer’s short-term memory. Color, line weight, scale, and placement are used to bring out the conceptual meaning of these “chunks”, all helping to match content to its hierarchy of importance. The viewer can easily navigate the chunks and understand their significance. - Better decision-making based on data
Business meetings that discuss visual data tend to be shorter and reach consensus more easily as compared to those that focus on only text or numbers. Data visualization helps to reach decisions faster and enables viewers to glean far better insights about patterns and trends.
With visualization, the benefits of data analytics are available to various roles throughout your organization, who may not be experts in the field. If you put the right data visualization systems in place, your sales staff can gain a better understanding of consumer behavior and perceptions even though they may not be experts at interpreting data themselves. Data visualization is a combination of technical analytics and creative storytelling, allowing you to create experts with the right tools and training.
You will get the best outcomes when visualizations are developed to best suit your business objectives. Some data visualizations help to analyze, while others present information in an interesting way. Some are designed to illustrate concepts, processes, or strategies for different kinds of viewers. Build your own based on your specific objectives, type of data, and needs of different stakeholders. - Audience Engagement
Viewers feel far more engaged when they are able to relate to data thanks to good visual presentation. Images produce emotional responses, so data visualization can help to drive opinion and action.
Visualization also enables communication and collaboration as multiple stakeholders can view, appreciate and discuss insights from data. We now expect data to be presented in easy-to-understand, visual methods. For example, when we want to know the performance of our own websites, we consult Google Analytics, which has charts that help us to understand the information far better than if it were in raw tabular form. As another example, consider sales spread over a geographical region, or retail outlet and distributor locations. It would certainly be more helpful for you to view this as a geospatial distribution than as descriptive text.
During sales presentations, data that showcases your strength, when presented visually, goes a long way in building credibility and persuading. Encourage your sales teams to share visual data that proves claims rather than just words.
Interactivity goes a long way in creating engagement. Can you create interactive visualizations that viewers can change, ask queries, and arrive at conclusions of their own? This helps to build more credibility about the data. - Reveals hidden patterns and deeper insights
Data visualization uncovers trends, patterns, and relationships that are not easily discernible from numerical data or traditional forms of representation. Deeper insights and interrelationships can be obtained through data visualization.
Sales forecasts made using data visualization tend to be more accurate than others. When it comes to consumer behavior, visualization helps to see a number of different factors and how they are related to each other, leading to a better understanding.
You can also use data visualization to understand your own operations, identify bottlenecks and pinpoint areas that need improvement. For instance, let’s say there are spikes in customer complaints. When the data is seen in conjunction with certain changes in the support staff, you may find correlation and possibly causes.
Visualizations are used to illustrate six analytical functions:
Distribution: Highlights the spread, center, and shape of data.
Comparison: The correlation, magnitude, or rankings between different dimensions.
Change over Time: Highlights how a measure changes over time.
Flow: Explores the path from one point to another.
Spatial: Exposes patterns related to position and location in data.
Part-to-Whole: Explores how much of the total population a particular part makes up.
As examples, in business, heat maps can be used to see the relationship between two factors, such as product sales in different regions, sales figures by individual rep. Flow maps are used to see the route for delivering consignments in logistics companies. A part-to-whole chart shows what percentage of total sales comes from one particular product.
A number of tools and techniques are available to create effective data visualizations. It’s important that you and your team understand the underlying principles, and select suitable tools. Above all, it’s important that data is presented without distortions. Layouts, colors, text, and dashboard interactivity also need to be designed carefully, to create data visualizations that will best serve your business objectives.



